pygmt.Figure
- class pygmt.Figure[source]
A GMT figure to handle all plotting.
Use the plotting methods of this class to add elements to the figure. You can preview the figure using
pygmt.Figure.showand save the figure to a file usingpygmt.Figure.savefig.Unlike traditional GMT figures, no figure file is generated until you call
pygmt.Figure.savefigorpygmt.Figure.psconvert.Examples
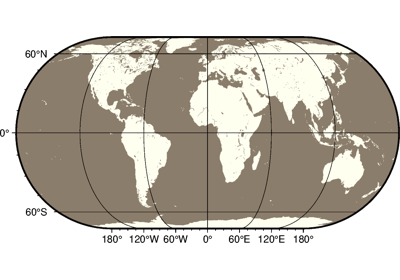
>>> import pygmt >>> fig = pygmt.Figure() >>> fig.basemap(region=[0, 360, -90, 90], projection="W15c", frame=True) >>> fig.savefig("my-figure.png") >>> # Make sure the figure file is generated and clean it up >>> import os >>> os.path.exists("my-figure.png") True >>> os.remove("my-figure.png")
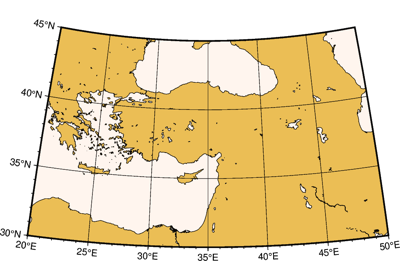
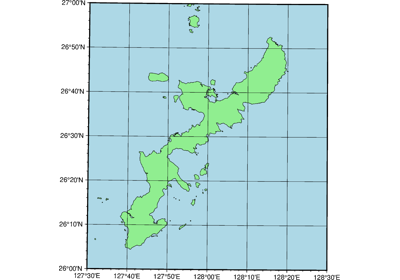
The plot region can be specified through ISO country codes (for example,
"JP"for Japan):>>> import pygmt >>> fig = pygmt.Figure() >>> fig.basemap(region="JP", projection="M7c", frame=True) >>> # The fig.region attribute shows the WESN bounding box for the figure >>> print(", ".join(f"{i:.2f}" for i in fig.region)) 122.94, 145.82, 20.53, 45.52
Methods Summary
|
Plot base maps and frames for the figure. |
|
Plot continents, shorelines, rivers, and borders on maps. |
|
Plot a gray or color scale-bar on maps. |
|
Contour table data by direct triangulation. |
|
Convert grids or images to contours and plot them on maps. |
|
Project and plot grids or images. |
|
Create 3-D perspective image or surface mesh from a grid. |
|
Plots a histogram, and can read data from a file or list, array, or dataframe. |
|
Place images or EPS files on maps. |
|
Create an inset figure to be placed within a larger figure. |
|
Plot legends on maps. |
|
Plot the GMT logo. |
|
Plot focal mechanisms. |
|
Plot lines, polygons, and symbols in 2-D. |
|
Plot lines, polygons, and symbols in 3-D. |
|
Convert [E]PS file(s) to other formats. |
|
Plot windrose diagrams or polar histograms. |
|
Save the figure to a file. |
|
Set the current subplot panel to plot on. |
|
Shift plot origin in x and/or y directions. |
|
Display a preview of the figure. |
|
Plot day-light terminators or twilights. |
|
Create multi-panel subplot figures. |
|
Reads (a,b,c[,z]) records from data and plots symbols at those locations on a ternary diagram. |
|
Plot or typeset text strings of variable size, font type, and orientation. |
|
Plot velocity vectors, crosses, anisotropy bars, and wedges. |
|
Plot z=f(x,y) anomalies along tracks. |